- Project Leader:Okumiya Kiyohito (Kyoto University, Center for Southeast Asian Studies)
- Collaborators:Kuzuhara Shigeki (Suzuka University of Medical Science, Faculty of Health Science)
- Kokubo Yasumasa (Mie University , Graduate School of Regional Innovation Studies)
- Eva Garcia del Saz (Kochi University, Center for International Collaboration)
- Matsubayashi Kozo (Kyoto University, Center for Southeast Asian Studies, Emeritus Professor)
- Fujisawa Michiko (Kyoto University, Center for Southeast Asian Studies)
- Hirata Yutaka (Yoshida Hospital, Cerebrovascular Research Institute, Department of Neurology)
Outline of Research
Only one previous follow-up study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Parkinsonism in Papua, Indonesia has been carried out since a survey undertaken in 1962-1981 by Gajdusek and colleagues. Therefore, to investigate the clinical epidemiology of ALS and Parkinsonism in the southern coastal region of Papua, we will examine the clinical characteristics and prevalence of the diseases in this region.
Description
Cases of ALS and Parkinsonism were clinically examined during a 2001-2016 survey in Bade and other villages along the Ia, Edera, Dumut and Obaa rivers in Papua, Indonesia.
We have been carrying out a survey of neurodegenerative diseases in Papua since 2001, and have identified a prevalence of ALS and Parkinsonism higher than the global average despite a decrease in ALS prevalence in Papua over the past 30–35 years.
The purpose of this study is to examine the association of clinical epidemiology with aging as well as with ecological and environmental changes in Papua.
It is noteworthy that contrary to the recent situation in Guam and Kii (Japan), there are still many cases showing pure ALS and an overlap of ALS, Parkinsonism and cognitive impairment in Papua. The changing patterns of a decrease in incidence of ALS and the increase in that of Parkinsonism in Papua might be caused by changes in environmental and socioeconomic factors. The study is expected to identify and isolate risk factors and contribute to understanding the etiology of these neurodegenerative diseases.
We will submit papers and hold workshops and symposiums with collaborators in Papua and Japan.
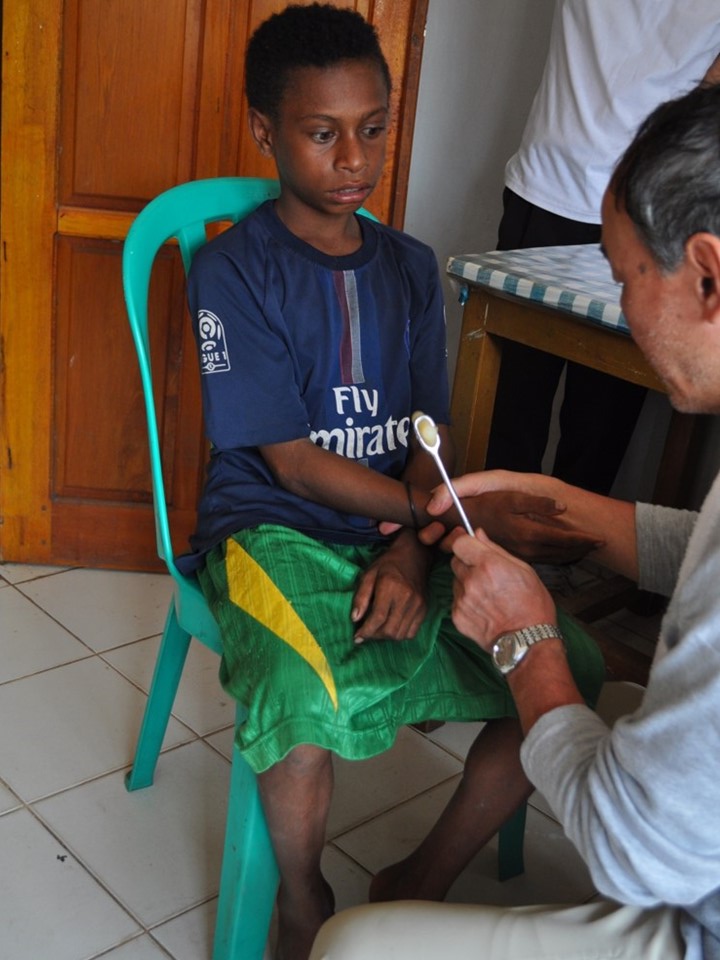 Physical examination of neurological case in Bade Clinic, March 2016. |
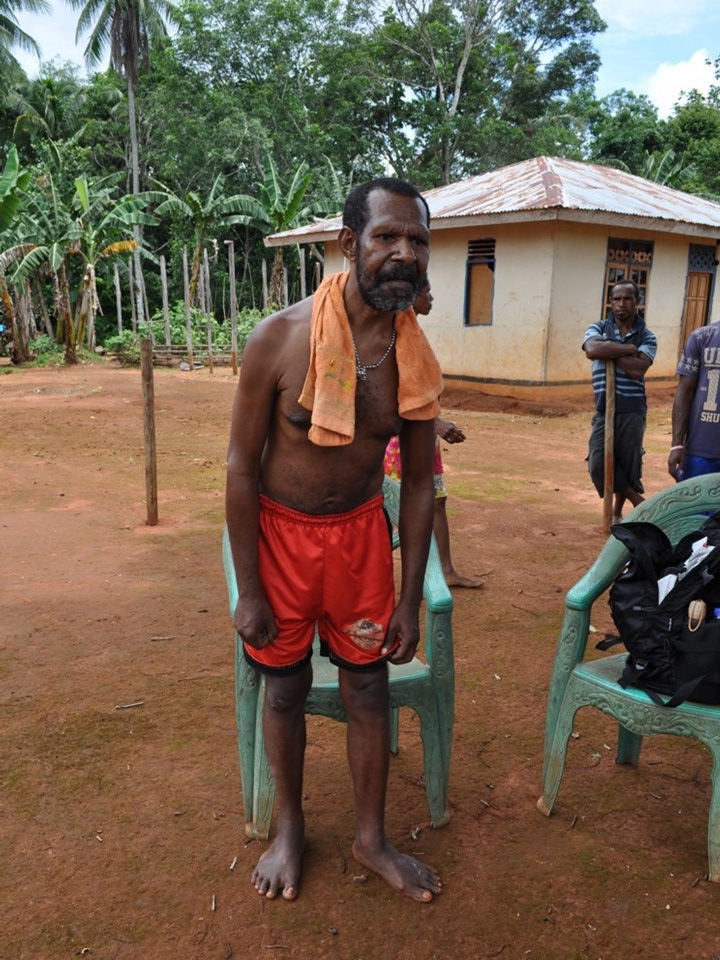 Home visit of Parkinsonian case, Ia River, March 2016. |
